Whole blood is composed of three primary constituents: Red Blood Cells (RBCs), White Blood Cells (WBCs), and Plasma. The function of the RBCs is to carry and transport oxygen (they are important for endurance athletes). WBCs fight infection. Diseases like leukemia, lymphoma, and HIV stem from problems with the WBC. Within the plasma are small cells called platelets. The platelets are best known for their importance in clotting blood. However, platelets also contain hundreds of proteins called growth factors which are critically important in the healing of injuries.
PRP is plasma with many more platelets than what is typically found in whole blood. By drawing whole blood and putting it through a centrifugation process, we are able to concentrate the platelets. The concentration of platelets — and, thereby, the concentration of growth factors — can be 5 to 10 times greater (or richer) than usual.
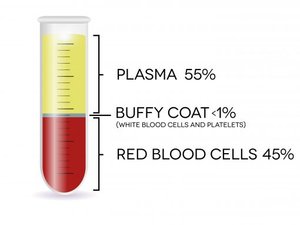
To develop a PRP preparation, blood must first be drawn from a patient (usually between 30 and 60cc of whole blood). The platelets are separated from the other blood cells and their concentration is increased during a process called centrifugation (ie. spinning the blood). The final PRP product is separated and injected back into the patient at the source of injury, ultimately augmenting the natural healing response of the body while expediting recovery.
What Conditions Are Treated With PRP? Is It Effective?
PRP has been studied extensively over the past few years. There are hundreds of studies published that review its effectiveness and compare it to previously used “gold standards” (ex. corticosteroids). PRP has been shown to be effective for these conditions and many others:
- Chronic Tendon Injuries (ex. Tennis Elbow, Golfer’s Elbow, Jumper’s Knee (Patella Tendinitis))
- Acute Tendon, Ligament, and Muscle Injuries (ex. Achilles Tendon Injuries)
- Osteoarthritis (Knee, Hip, Shoulder, etc)
- Rotator Cuff tears in the shoulder
- Bursitis (Hip, Knee, Shoulder)
Studies Supporting the use of PRP:
Osteoarthritis:
- Efficacy of Intra-articular Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Arthroscopy (2016).
- Platelet-rich plasma in the management of articular cartilage pathology: a systematic review. CJSM (2014).
- Hyaluronic Acid Versus Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Prospective, Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Clinical Outcomes and Effects on Intra-articular Biology for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. AJSM (2017).
- Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid, Separately and in Combination, for Hip Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Study. AJSM (2016).
- Short-term outcomes of platelet-rich plasma injection for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. KSSTA (2016).
- Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arthroscopy (2017).
- The temporal effect of platelet-rich plasma on pain and physical function in the treatment of kneeosteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res (2017).
- Hyaluronic Acid Versus Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Prospective, Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Clinical Outcomes and Effects on Intra-articular Biology for theTreatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. AJSM (2017).
- Does Intra-articular Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection Provide Clinically Superior Outcomes Compared With Other Therapies in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis? A Systematic Review of Overlapping Meta-analyses. Arthroscopy (2015).
- Safety and Efficacy of Intra-articular Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Patients With AnkleOsteoarthritis. Foot Ankle Int (2017).
Tendinopathy and Tendonitis of the Elbow:
- Platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection for recalcitrant lateral epicondylitis: clinical and ultrasonographic evaluation. J Orthop Surg (2015).
- Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for chronic tennis elbow: a double-blind, prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial of 230 patients. AJSM (2014).
- Platelet-rich plasma versus autologous blood versus steroid injection in lateral epicondylitis: systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Orthop Traumatol (2016).
- Single injection of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for the treatment of refractory distal biceps tendonitis: long-term results of a prospective multicenter cohort study. KSSTA (2016).
- Ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injection for distal biceps tendinopathy. Shoulder and Elbow (2015).
- Growth factor-based therapies provide additional benefit beyond physical therapy in resistant elbow tendinopathy: a prospective, single-blind, randomised trial of autologous blood injections versus platelet-rich plasma injections. Br J Sports Med (2011).
Hip Conditions: Tendinopathy and Bursitis
- The Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections in Gluteal Tendinopathy: A Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Trial Comparing a Single Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection With a Single Corticosteroid Injection. AJSM (2018).
- Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections With Needle Tenotomy for Gluteus Medius Tendinopathy: A Registry Study With Prospective Follow-up. Orthop J Sports Med (2016).
- Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: Percutaneous Tendon Fenestration Versus Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Treatment of Gluteal Tendinosis. J Ultrasound Med (2016).
Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy of the Shoulder:
- Effects of bone marrow aspirate concentrate and platelet-rich plasma on patients with partial tear of the rotator cuff tendon. J Orthop Surg Res (2018).
- The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Tendon and Ligament Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis With Bias Assessment. AJSM (2017).
- Impact of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Arthroscopic Repair of Small- to Medium-Sized Rotator CuffTears: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Orthop J Sports Med (2016).
- Does application of moderately concentrated platelet-rich plasma improve clinical and structural outcome after arthroscopic repair of medium-sized to large rotator cuff tear? A randomized controlled trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2016).
- Leukocyte-Reduced Platelet-Rich Plasma Normalizes Matrix Metabolism in Torn Human Rotator Cuff Tendons. AJSM (2015).
- The effect of subacromial injections of autologous conditioned plasma versus cortisone for the treatment of symptomatic partial rotator cuff tears. KSSTA (2016).
- Platelet-rich plasma for arthroscopic repair of medium to large rotator cuff tears: a randomized controlled trial. AJSM (2015).
Dr. Dold is widely considered an expert in PRP and other biologic therapies. These treatments are minimally invasive and can be performed in clinic, often negating the need for surgery. If you are considering PRP as a treatment option for you, please contact us for a consultation: 469.850.0680.


